Next-Generation Aircraft: Innovations Shaping the Skies

Next-Generation Aircraft: Innovations Shaping the Skies
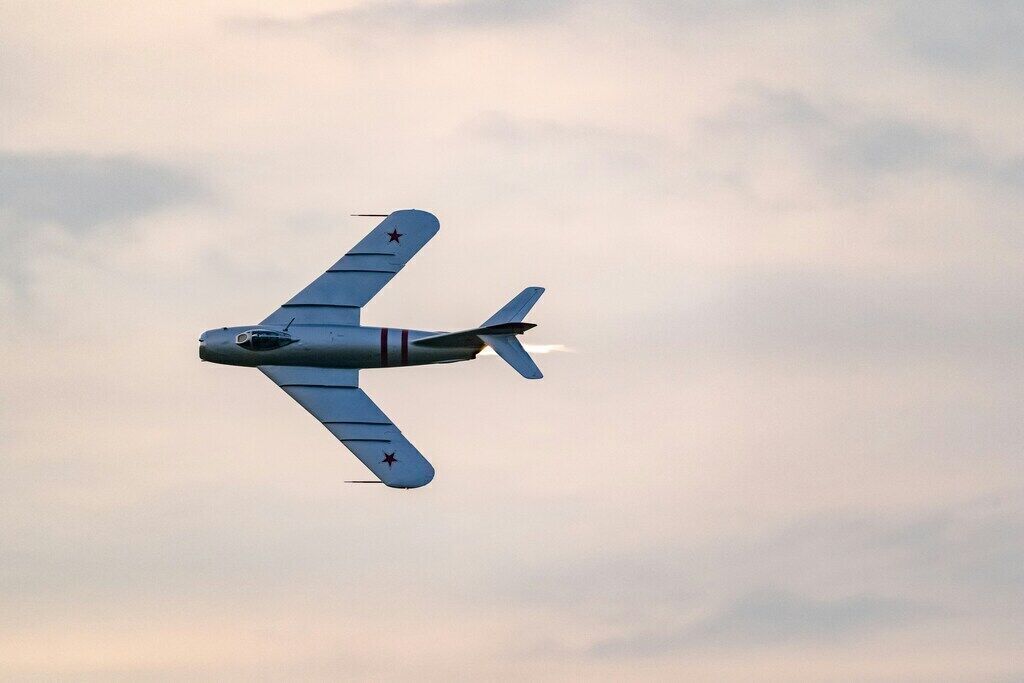
With the rapid advancement of technology, the aviation industry is entering an unprecedented era of innovation. Next-generation aircraft are not only breaking new ground in design and performance but also demonstrating tremendous potential in environmental sustainability, efficiency, and safety. This article explores the core technologies behind these aircraft, their development trends, and their profound impact on the future of aviation.
1. Definition and Key Features of Next-Generation Aircraft
Next-generation aircraft typically refer to airplanes that incorporate advanced materials, new propulsion systems, intelligent control technologies, and innovative design concepts. Compared to traditional aircraft, they feature:
- Lightweight Materials : Extensive use of carbon fiber composites and high-performance alloys makes the aircraft structure lighter and stronger, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
- High-Efficiency Propulsion Systems : Including turbofan engines, electric, or hybrid propulsion systems, which significantly reduce fuel consumption and noise pollution.
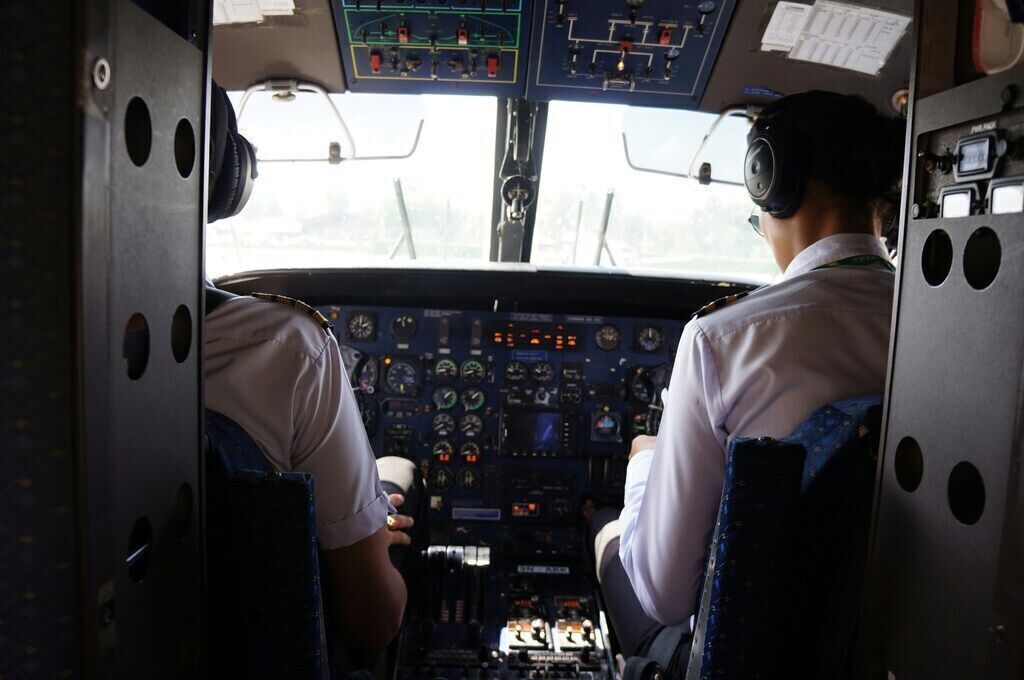
- Intelligent Avionics Systems : Modern aircraft are equipped with advanced flight management systems (FMS), autopilot systems, and intelligent sensors, enhancing flight safety and operational convenience.
- Eco-Friendly Design : Through optimized aerodynamics, reduced fuel consumption, and sustainable materials, next-generation aircraft aim to minimize aviation’s environmental impact.
2. Advanced Aerodynamic Design
Aerodynamics plays a critical role in aircraft performance. Next-generation aircraft utilize innovative designs to significantly improve lift-to-drag ratios, achieving higher fuel efficiency. Examples include:
- Optimized Wing Shapes : Complex curved surfaces and wingtip devices reduce induced drag and improve lift efficiency.
- Blended Wing-Body Design : Concepts like the “flying wing” or blended fuselage design reduce drag and increase fuel economy.
- Variable Geometry Structures : Some new aircraft feature adjustable wing shapes or flap systems to optimize aerodynamic performance at different flight stages.
These technologies not only enable aircraft to fly farther and faster but also lower operational costs and environmental footprints.
3. Electric and Hybrid Propulsion Technology
Traditional jet engines consume large amounts of fuel and emit significant greenhouse gases. To address these challenges, the aviation industry is increasingly exploring electric and hybrid propulsion systems:
- Fully Electric Aircraft : Powered entirely by electric motors and batteries, these aircraft produce zero in-flight emissions and are ideal for short regional routes.
- Hybrid-Electric Systems : Combine conventional engines with electric motors, offering improved efficiency and reduced emissions for longer flights.
- Hydrogen-Powered Propulsion : Some experimental aircraft are being designed to use hydrogen fuel cells, which produce only water as a byproduct, presenting a promising pathway toward sustainable aviation.
The development of these propulsion technologies not only reduces the environmental impact of flying but also paves the way for quieter, more efficient aircraft.
4. Advanced Materials and Structural Innovations
Material science has become a cornerstone of next-generation aircraft development. Key innovations include:
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP) : These composites are lighter and stronger than aluminum, enabling weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency.
- Titanium and High-Strength Alloys : Used in critical structural components to withstand extreme stress while minimizing weight.
- 3D-Printed Components : Allow for complex, lightweight parts that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve, reducing production time and costs.
By integrating these materials, manufacturers are able to create aircraft that are not only lighter and more efficient but also more durable and safer.
5. Digitalization and Intelligent Avionics
Modern aircraft increasingly rely on digital technologies for performance optimization and safety:
- Advanced Flight Management Systems (FMS) : Automate complex flight planning and navigation tasks, reducing pilot workload.
- Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Systems : Enhance situational awareness and support decision-making in real time.
- Smart Sensors and Predictive Maintenance : Enable continuous monitoring of aircraft components, predicting failures before they occur and improving safety and operational efficiency.
The integration of these digital systems transforms the pilot’s role from direct operator to system manager, ensuring safer and more efficient flights.
6. Environmental Sustainability
Reducing the environmental impact of aviation is a critical goal for next-generation aircraft:
- Lower Fuel Consumption : Aerodynamic improvements and lightweight materials reduce fuel usage.
- Reduced Emissions : Hybrid, electric, and hydrogen-powered propulsion systems significantly cut greenhouse gas emissions.
- Noise Reduction Technologies : Engine designs and airframe optimizations reduce noise pollution, particularly near airports.
Sustainability in aviation is no longer optional; it is becoming a central driver of innovation and regulatory compliance.
7. Challenges and Future Prospects
While next-generation aircraft offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges:
- High Development Costs : Advanced materials and propulsion systems require significant investment.
- Energy Storage Limitations : Battery technology currently limits the range of electric aircraft.
- Regulatory Hurdles : New technologies must undergo rigorous testing and certification processes before entering commercial service.
Despite these challenges, the future is promising. With continuous investment and research, next-generation aircraft are expected to redefine air travel, offering safer, cleaner, and more efficient flights.
Conclusion
Next-generation aircraft are set to revolutionize the aviation industry. Through innovations in aerodynamics, propulsion, materials, and digital systems, these aircraft promise higher efficiency, lower environmental impact, and enhanced safety. As technology continues to evolve, the skies of the future will be shaped by these groundbreaking designs, marking a new era in aviation history.